Updates are necessary to maintain the security and reliability of Windows 11. You should ensure that devices are receiving updates, know how to review installed updates, and find more information regarding an update.
After you have created your Windows 11 Update Rings, you can manage them with Intune. Select the appropriate update ring, and on the Overview page, you can view the assignment status, showing that the ring has been successfully assigned to one group, and take the following actions to manage the ring:
- Delete Stops enforcing the settings of the Update Ring and removes its configuration from Intune. The settings on devices that were assigned to the Update Ring remain in place.
- Pause Prevents assigned devices from receiving either Feature Updates or Quality Updates for up to 35 days from the time you pause the ring. Pause functionality automatically expires after 35 days.
- Resume Used to restore an Update Ring that was paused.
- Extend When an Update Ring is paused, you can select Extend to reset the pause period.
- Uninstall Use Uninstall to uninstall (roll back) the latest Feature Update or Quality Update on a device running Windows 11.
You can also modify the settings contained within an Update Ring by selecting Properties under the Manage heading and then amending the settings.
View update history
You can also review and remove any specific updates on an individual computer. Follow these steps to view your update history and see which Windows updates failed or were successfully installed on your Windows 11 device:
- Open the Settings app and click Windows Update.
- In Windows Update, click Update History.
- On the Update History page, as shown in Figure 3-52, you can see a list of your installed Windows updates.
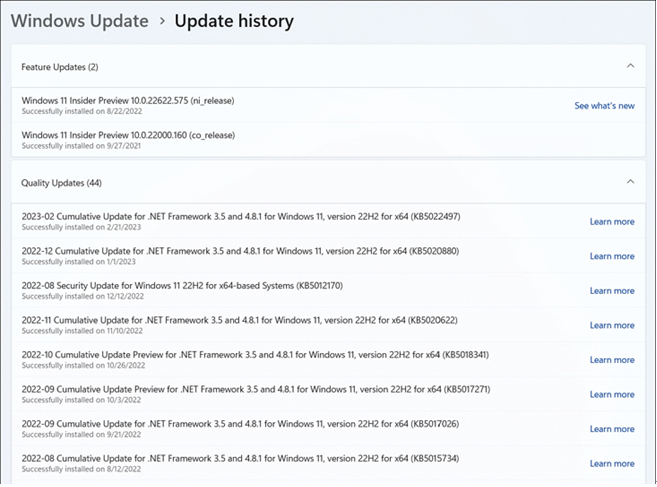
FIGURE 3-52 View Update History
- Click one of the successfully installed updates to see more details about it.
- In the bottom part of the screen, you can view Definition Updates, which relate to Microsoft Defender Antivirus and threat protection, and Other Updates.
Each update contains a summary of the payload. If you click the Update link, you are directed to the detailed Knowledge Base description on the Microsoft support pages relating to the update, which allows you to review the details about the update. You can also remove any updates you want. Click Uninstall updates, and then review the returned list. Choose Uninstall for any updates you want to remove.
Need More Review? Windows 11 Update History
Microsoft publishes the contents of each Windows 11 update for you to review and understand what is contained in each periodic software update. View this list at https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/topic/windows-11-version-22h2-update-history-ec4229c3-9c5f-4e75-9d6d-9025ab70fcce.