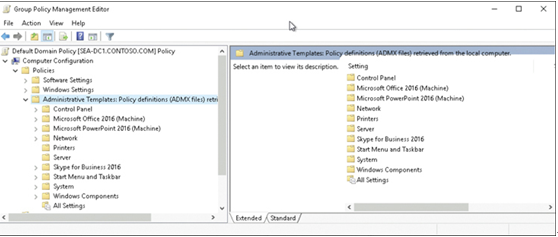
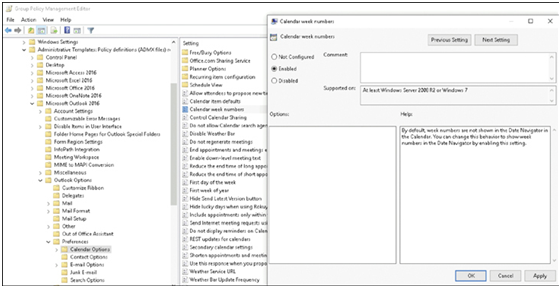
An organization with many apps can become overwhelming for users. To help users find an app in the company portal, you can assign apps to one or more categories, such as Accounting apps or Marketing apps.
When adding apps, you can assign a category in Intune using the following procedure:
- Sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center as a Global Administrator.
- Select Apps, then select App categories.
- The App categories pane displays a list of current categories.
- To add a category, select Add in the Create category pane, and then provide a name for the category.
- To edit a category, select the ellipsis (…) next to the category, and then select Pin to dashboard or Delete.
- Select Create.
Add Android store apps to Microsoft Intune
Use the following procedure to add an Android store app to Intune:
- Sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center as a Global Administrator.
- Select Apps > All apps > Add.
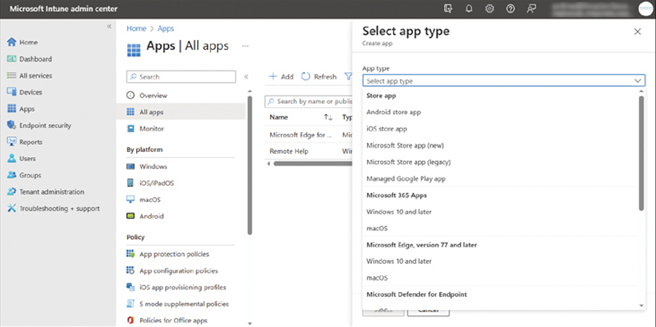
- In the Select app type pane, under Store app, select Android store app.
- Click Select.
- To configure the app information for the Android app, you must provide the Google Play store’s app details. (The Google Play store is located at https://play.google.com.)
- In the App information page, add the app details, as shown in Figure 4-18:
• Name
• Description
• Publisher
• Appstore URL
• Minimum operating system
• Category (Optional)
• Show this as a featured app in the Company Portal
• Information URL (Optional)
• Privacy URL (Optional)
• Developer (Optional)
• Owner (Optional)
• Notes (Optional)
• Logo (Optional)
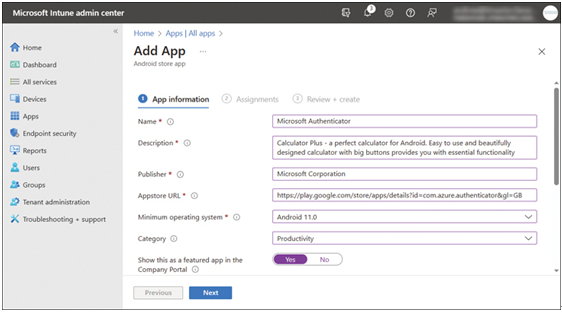
FIGURE 4-18 Adding a Windows 10 Line-of-business app
- Select Next.
- On the Assignments page, select the group assignments for the append and select Next.
- On the Review + create page, review the values and settings you entered for the app and select Create to add the app to Intune.
- The app’s Overview blade is displayed.