The Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management Dashboard in Microsoft 365 Defender provides a wide variety of useful information that can help you identify issues and respond to those issues. Figure 3-64 displays a typical dashboard for an enterprise organization.
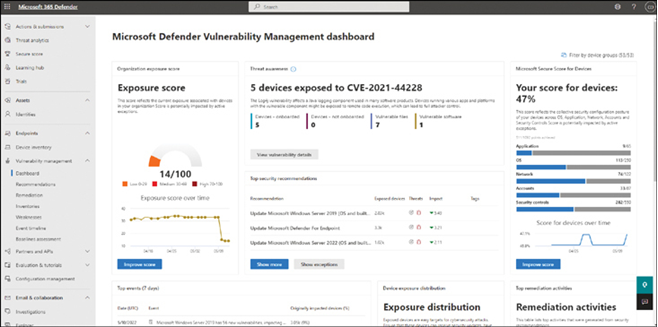
FIGURE 3-64 Reviewing the Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management Dashboard
Use the information summary in Table 3-20 to determine how to use the Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management Dashboard.
TABLE 3-20 The features and elements in the Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management Dashboard
| Area | Description |
| Selected device groups (#/#) | Enables you to filter the data you want to review. |
| Organization exposure score | Displays a headline figure that indicates your organization’s device exposure to threats and vulnerabilities. Click Improve score to review insights that can help you improve the score and your security posture. |
| Microsoft Secure Score for Devices | Enables you to review the security relating to your organization’s operating system, applications, network, accounts, and security controls. Again, you can use the Improve score link to review insights and suggestions for improvements in this area. |
| Device exposure distribution | Displays the number of devices that are exposed to threats based on their configuration. Presented graphically as a doughnut chart. By selecting sections of the chart, you can review •Device names •Exposure level and risk levels •Details such as operating system, health state, and tags |
| Expiring certificates | Displays a list of expired certificates or those imminently expiring in the next 30, 60, or 90 days. |
| Top security recommendations | Review top recommendations for improving the security posture of your organization’s devices. |
| Top vulnerable software | Review your software inventory. Identify those apps with security vulnerabilities. |
| Top remediation activities | Review the security remediations that are recommended in one convenient location. This enables you to track changes as you make them more easily. |
| Top exposed devices | Review devices and their details that have a high security exposure score. From Device details, you can •Manage tags •Initiate automated investigations •Initiate a live response session •Collect an investigation package •Run antivirus scan •Restrict app execution •Isolate devices |
Need More Review? Dashboard Insights
To learn more about the dashboard in Microsoft Defender, refer to the Microsoft website at https://learn.microsoft.com/microsoft-365/security/defender-vulnerability-management/tvm-dashboard-insights.
Chapter summary
- Intune device configuration policies are used to configure device settings using MDM.
- Intune can deploy PowerShell scripts to Windows devices using an MDM extension. This allows administrators to deploy Win32 apps if required.
- Scope tags are used to assign and filter Intune policies to specific Azure AD groups.
- You can configure custom policies with Intune by configuring an Open Mobile Alliance Uniform Resource Identifier (OMA-URI) policy.
- Microsoft Defender Credential Guard requires a TPM and virtualization features to be enabled in a 64-bit edition of either Windows 11 Enterprise or Windows 11 Education.
- Microsoft Defender Exploit Guard consists of four components: Exploit Protection, Attack Surface Reduction Rules, Network Protection, and Controlled Folder Access.
- Microsoft Defender Application Guard has similar requirements to Credential Guard, enabling you to open new browser windows in a virtualized environment.
- Microsoft Defender Application Control lets you determine which apps are safe to run in your organization.
- Most of these Windows Defender features are managed through Windows PowerShell, Group Policy, and Microsoft Intune.
- Automatic enrollment lets you enroll Windows devices when they register with or join Azure AD.
- Device Enrollment Manager Accounts enable a specified account to enroll up to 1,000 devices.
- There are a number of ways to enroll Windows devices:
- Add a Work Or School account
- Enroll In MDM Only (user-driven)
- Azure AD Join during OOBE
- Azure AD Join using Windows Autopilot
- Enroll In MDM only (using a Device Enrollment Manager)
- Azure AD Join using bulk enrollment
- To enroll Android and iOS devices, you can download the Company Portal app from the relevant device store and sign in to the app using an organizational or school account.
- Log Analytics requires an Azure subscription.
- Windows Update Delivery Optimization is a method of peer-to-peer sharing of Windows update files.
- Administrators can use Intune to centrally configure and manage Windows Update behavior and Windows Update Delivery Optimization settings.
- Scope tags enable you to more specifically target the application of configuration profiles.
- You can configure Kiosk mode by using the Settings app and by using Intune.
- The Microsoft Tunnel for Intune enables iOS and Android devices to access your on-premises resources and apps.
- You can use Endpoint analytics to gain insights into Startup Performance, Proactive remediations, Recommended software, and Application reliability.
- You configure the application of updates for iOS, macOS, and Windows by using update rings in Intune.
- You configure the application of updates for Android by using a Device Restrictions configuration profile.
- Microsoft Defender Exploit Guard provides four functions: Exploit protection, Attack surface reduction rules, Network protection, and Controlled folder access.
