It’s important to consider the available authentication options. You can use the following methods:
- TPM + startup PIN + startup key This is the most secure combination. The encryption key is stored on the TPM chip. The user might find this option cumbersome because this requires multiple authentication tasks.
- TPM + startup key The encryption key is stored on the TPM chip. The user must insert a USB flash drive containing a startup key.
- TPM + startup PIN The encryption key is stored on the TPM chip. The user needs to enter a PIN to unlock the device.
- Startup key only The user needs to insert a USB flash drive with the startup key on it. The device doesn’t need to have a TPM chip. The BIOS must support access to the USB flash drive before the operating system loads.
- TPM only The encryption key is stored on the TPM chip, and no user action is required.
With all the BitLocker authentication methods, the drive is encrypted until unlocked. When the BitLocker encrypted drive is in recovery mode, you can also unlock the drive by using either the recovery password or recovery key:
- Recovery password This is a 48-digit number typed on a regular keyboard or by using the function keys (F1-F10) to input the numbers.
- Recovery key This is an encryption key created when the BitLocker is first employed and is for recovering data encrypted on a BitLocker volume. Often the encryption key is stored on removable media.
Because the TPM chip and BitLocker protect the hard drive, administrators can also configure BitLocker to operate without additional unlock steps, so long as the device (and TPM) recognize the drive, it will be unlocked.
Configure BitLocker with Intune
If you have many devices on which you want to enable and manage BitLocker, you can use Microsoft Intune. To configure BitLocker, use the following procedure:
- Open Microsoft Intune admin center.
- Navigate to Endpoint security and select Disk encryption.
- In the details pane, select Create Policy.
- On the Create a profile page, displayed in Figure 3-53, in Platform, select Windows 10 and later.
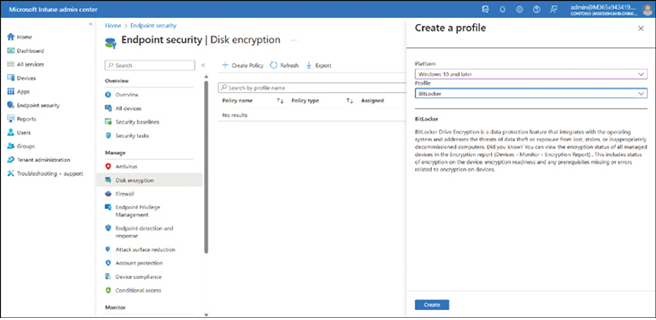
FIGURE 3-53 Creating a BitLocker profile in Intune
- In the Profile, select BitLocker, and then select Create.
- On the Create profile page, on the Basics tab, enter a Name and Description, and then select Next.
- On the Configuration settings tab, shown in Figure 3-54, configure the following settings, and then select Next:
• BitLocker – Base Settings Including whether to enable full disk encryption for OS and fixed data drives.
• BitLocker – Fixed Drive Settings Including drive recovery settings and encryption methods for fixed data drives.
• BitLocker – OS Drive Settings Including whether Startup authentication is required, such as TPM startup options as discussed earlier. You can also define the system drive recovery options.
• BitLocker – OS Drive Settings Including blocking write access to removable data drives not protected by BitLocker.
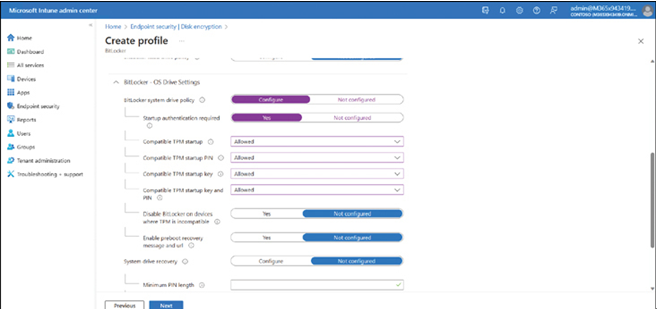
FIGURE 3-54 Configuring BitLocker – OS Drive Settings in an Intune profile
- Optionally, configure scope tags, and then, in the Assignments tab, assign the profile to the required groups.
- Finally, on the Review + create tab, select Create.
You can also configure BitLocker settings in Intune by using Configuration Profiles in the Devices node. Use the following procedure:
- Select Devices, select Windows, and then select Configuration profiles.
- Select Create profile, and in the Platform list, select Windows 10 and later.
- In the Profile type list, select Templates. You can now choose either:
• Administrative templates Choose this option to use an interface that’s broadly similar to that used when configuring GPO settings. Create the profile as usual, and on the Configuration Settings tab, expand Computer Configuration > Windows Components > BitLocker Drive Encryption > Operating System Drives and configure the required values. Then complete the process of configuring and assigning the profile. The advantage of configuring BitLocker this way is that you can combine settings with others which are also configurable in the Administrative Template profile.
• Endpoint protection You can use Endpoint Protection profiles to configure a range of security settings, including those for BitLocker. Create the profile in the usual way, and on the Configuration settings tab, in addition to any other settings, make sure to expand Windows Encryption. You can then require BitLocker encryption and go on to configure BitLocker base settings, OS drive settings, and fixed data-drive settings. Complete the process of configuring and assigning the profile.
